Spatial Metabolomics in Oncology: Transforming Cancer Diagnostics with Mass Spectrometry Imaging
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) has emerged as a powerful tool for mapping analytes in biological tissues. By integrating the label-free specificity of mass spectrometry with the detailed spatial information from traditional histology, hundreds of metabolites can be simultaneously imaged within tumors. MSI generates highly detailed metabolite maps, enabling comparative analyses of tumor cores, margins, and adjacent healthy tissues. This facilitates the identification of biomarkers, disease patterns, therapeutic targets, drug delivery pathways, and mechanisms of drug action. This article series highlights the roles of metabolites in cancer progression, discusses applications of spatial MSI in oncology, and explores metabolic signatures and research directions in cancer spatial metabolomics.
Applications of Spatial Metabolomics in Cancer Research
Tumor metabolism exhibits spatial heterogeneity, with distinct metabolic profiles observed in normal tissues, lesions, and peri-tumoral regions. MSI serves as a critical tool for cancer tissue metabolomics by embedding spectral data into spatial coordinates, capturing not only metabolite intensities but also their precise localization. This allows visualization of metabolite distributions across tissues. Key applications include:
- Tumor Biomarker Discovery: Facilitating diagnosis, subtyping, and grading.
- Tumor Margin Delineation: Enhancing pathological accuracy for surgical planning.
- Pharmacokinetics: Mapping drug distribution and optimizing delivery systems.
Tumor Spatial Metabolomics Biomarker Research (Diagnosis, Subtyping, and Grading)
Accurate biochemical biomarkers are essential for clinical diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment strategies. Precise delineation of tumor boundaries minimizes recurrence risks and reduces complications from over-resection of healthy tissue. Prognostic and therapeutic decisions rely heavily on accurate tumor classification by type and grade. Early identification of molecular markers holds significant clinical value. MSI-based approaches have been widely employed to identify and stratify diverse cancer types.
MSI tumor lipid biomarkers
|
Disease |
Compounds |
MSI Technologies |
References |
|
Breast Cancer |
PC, FA |
MALDI |
Fine needle aspiration combined with matrix-assisted laser desorptionionization time-of-fight/mass spectrometry to characterize lipid biomarkers for diagnosing accuracy of breast cancer |
|
Kidney Cancer |
PL, Cer |
MALDI |
MALDI orbitrap mass spectrometry profiling of dysregulated sulfoglycosphingolipids in renal cell carcinoma tissues. |
|
Ovarian Cancer |
PC, PG, CL, Cer |
DESI |
Nondestructive tissue analysis for ex vivo and in vivo cancer diagnosis using a handheld mass spectrometry system. |
|
Colon Cancer |
PE, PI, PG, PS |
3-D-DESI |
Deep learning and 3D-DESI imaging reveal the hidden metabolic heterogeneity of cancer |
|
Prostate Cancer |
PL |
DESI |
Diagnosis of prostate cancer by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometric imaging of small metabolites and lipids. |
|
Lymphoma |
PE, PG, PS, PI, Cer, DAG, FA |
DESI |
Detection of metastatic breast and thyroid cancer in lymphnodes by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging. |
|
Mastitis |
PI, PE, PG, PS |
DESI |
Multicenter study using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging for breast-cancer diagnosis. |
|
Colon Cancer |
PE |
MALDI |
Tissue-selective alteration of ethanolamine plasmalogen metabolism in dedifferentiated colon mucosa |
|
Colon Cancer |
PC, CS, SM, FA |
AP-MALDI/SIMS |
Correlative mass spectrometry imaging, applying time-of-fight secondary ion mass pectrometry and atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization to a single tissue section. |
|
Kidney Cancer |
PI, PS |
MALDI |
HILIC/ESI-MS determination of gangliosides and other polar lipid classes in renal cell carcinoma and surrounding normaltissues |
|
Brain Cancer |
PG, SL |
MALDI |
Rapid discrimination of pediatric brain tumors by mass spectrometry imaging. |
|
Lung Cancer |
PL |
MALDI |
Multisensor imaging from sample preparation to integrated multimodal interpretation of LA-ICP-MS and MALDI-MS imaging data. |
|
Lymphoma |
PI, SM, PE, CL |
MALDI |
Specific lipid and metabolic profiles of R-CHOP-resistant diffuse large B-cell lymphoma elucidated by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry imaging and in vivo imaging |
|
Thyroid Cancer |
PC, PA, SM |
MALDI |
Discrimination of papillary thyroid cancer from non-cancerous thyroid tissue based on lipid profiling by mass spectrometry imaging. |
|
Skin Cancer |
PC, PG, PS, PI, FA |
DESI |
Distinguishing malignant from benign microscopic skin lesions using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging. |
|
Pancreatic Cancer |
FA, PC, DAG, SM, PE |
SIMS |
Analysis of the Myc-induced pancreatic beta cell islet tumor microenvironment using imaging ToF-SIMS. |
|
Breast Cancer |
PI, PS, SM |
SIMS |
Lipid heterogeneity resulting from fatty acid processing in the human breast cancer microenvironment identified by GCIB-ToF-SIMS imaging. |
|
Lung Cancer |
PC |
MALDI |
The Ratios of monounsaturated to saturated phosphatidylchiolines in lung adenocarcinoma microenvironment analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and imaging mass spectrometry |
|
Brain Cancer |
PA, PE, PS, PI |
3-D-MALDI |
Three-dimensional mass spectrometry imaging identifies lipid markers of medulloblastoma metastasis. |
|
Kidney Cancer |
FA |
DESI |
Discovery of lipid biomarkers correlated with disease progression in clear cell enal cell carcinoma using desorption electrospray ionization imaging mass spectrometry |
|
Brain Cancer |
PI, ST |
MALDI |
Rapid MALDI mass spectrometry imaging for surgical pathology. |
Tumor Margin Delineation with MSI
Conventional frozen section histology faces limitations in sensitivity, specificity, and inter-observer variability, requiring expert pathologist evaluation. MSI overcomes these challenges by spatially resolving small-molecule distributions in tissue specimens. Co-registration of MSI data with adjacent H&E-stained slides enhances diagnostic precision and supports AI-driven pathology. In gliomas and breast cancer specimens, MSI combined with t-SNE dimensionality reduction resolved histologically ambiguous structures, improving frozen section diagnostic accuracy.
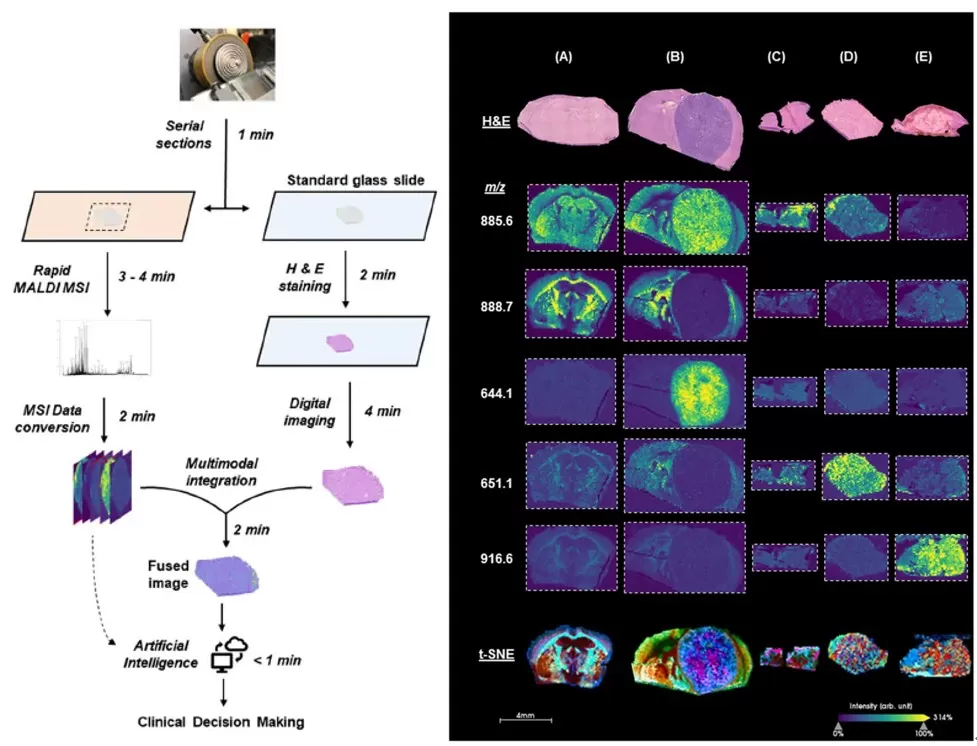
Histological and spatial mass spectrometry image visualization methods and results
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Distribution in Cancer
Systemic cancer therapy failures often stem from inadequate drug concentration or uneven distribution within tumors. MSI enables "precision pharmacology" by imaging drug distribution in tissues, informing optimal dosing, timing, drug combinations, and delivery systems in preclinical studies. Enhanced MSI speed, sensitivity, and resolution now permit analysis of tumor spheroids, revealing drug penetration into tumor subpopulations and niche microenvironments.
The integration of MSI with reproducible tumor models and AI-driven analytics holds immense potential for:
- Biomarker Screening: Refining cancer diagnosis and subtyping.
- Clinical Translation: Guiding personalized therapies and monitoring treatment responses.
Spatial metabolomics via MSI is revolutionizing oncology research by bridging molecular insights with spatial context. Its applications in biomarker discovery, surgical planning, and pharmacokinetics underscore its transformative role in advancing cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.


